The cloud computing landscape has undergone rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements and the exponential growth of both business and consumer demands. As we approach 2025, the cloud computing industry is poised to unveil a wealth of promising opportunities. Forward-thinking businesses must seize these prospects promptly to remain competitive. These advancements will not only optimize current capabilities but also introduce groundbreaking technological paradigms that will redefine the business landscape.
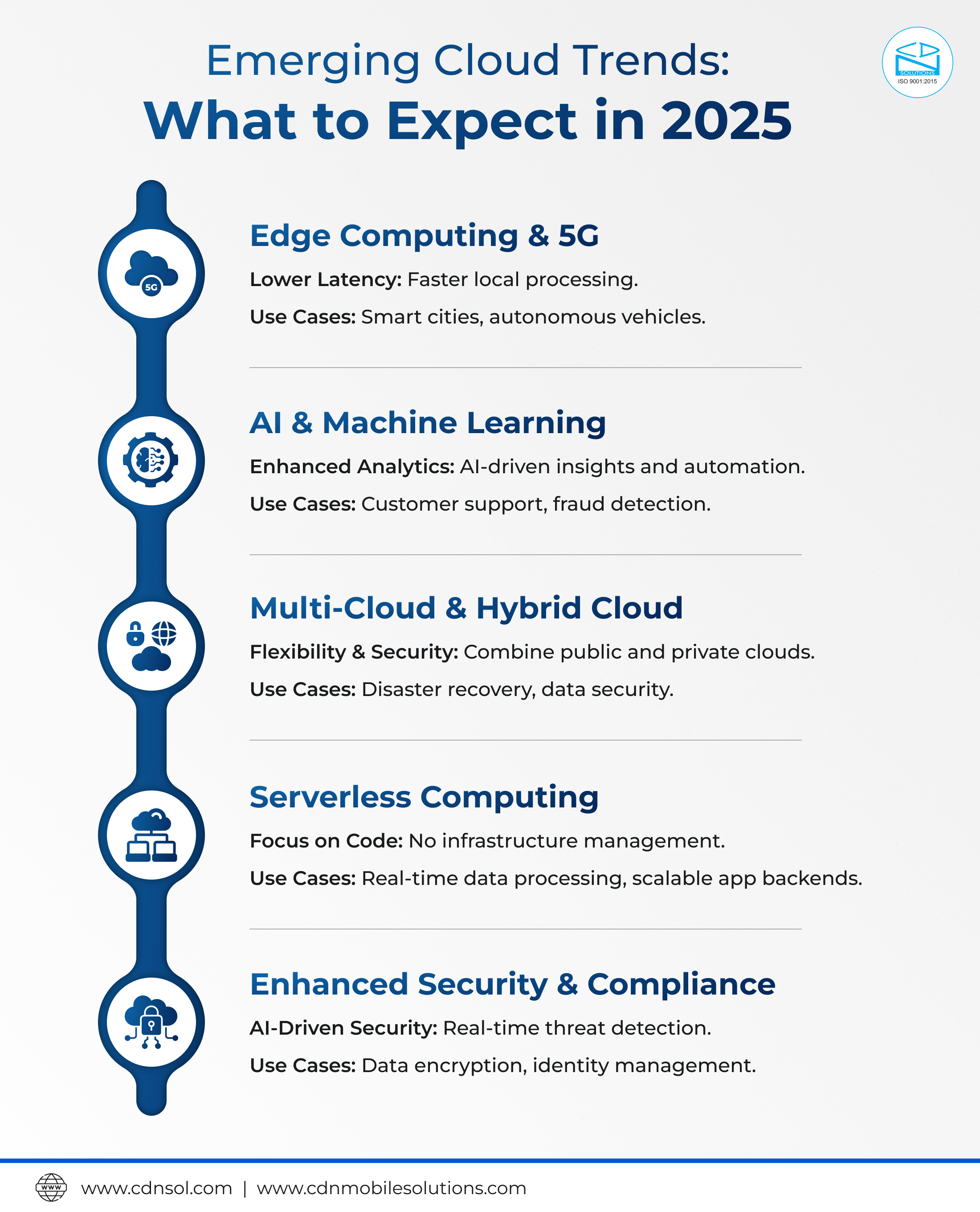
Table of Contents
Edge Computing and the Rise of 5G
Edge computing can be described as the act of processing data closer to the source of the data than relying on centralized data centers. The process reduces latencies, increases performance, and eases the process of real-time processing. The concept of edge computing has, with the rise in the number of Internet of Things devices and the introduction of 5G networks, been of growing significance.
5G embeds much higher data speeds, lower latency, and way higher capacity than what mobile networks offered in the past. These capabilities can be well leveraged for the proliferation of edge computing solutions supporting applications requiring real-time processing and low latencies, for example, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation.
Benefits of Edge Computing
- Lower Latency: Edge computing decreases latency by computing data closer to the source, providing faster responses.
- Greater Reliability: Edge computing makes systems less reliant on centralized data centers and more resilient to failure and network outages.
- Better Security: Processing data at the edge enhances security by reducing the amount of sensitive information transmitted over the network.
Use Cases
- Autonomous Vehicles: Real-time processing of sensor and video data at the edge is necessary to make self-driving cars safe for the road.
- Smart Cities: Real-time monitoring and control of city infrastructure include traffic lights, surveillance, and environmental sensors.
- Industrial Automation: Data processing for manufacturing optimization can take place at the edge, with real-time decision-making.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML are set to revolutionize cloud computing by making it much more intelligent and efficient. Cloud providers are weaving in AI and ML capabilities, and the tools and services offered by them bring the special features enabled by these technologies. Businesses thus have access and can make use of them without having to gain any further knowledge in these areas.
Key AI and ML Services
- AutoML (Automated Machine Learning)
- Simplifies machine learning model development and deployment.
- Makes the underlying technology available to a much wider community.
- Examples: Google Cloud AutoML and Azure Machine Learning.
- AI-Powered Analytics
- AI and ML enhance the quality of data analytic services.
- Provides deep insights and predictions with highly accurate results.
- Examples: AWS Athena and Google BigQuery.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- NLP cloud-based services offer to process and analyze text data.
- Perform sentiment analysis.
- Develop conversational interfaces.
- Examples: Amazon Comprehend and Azure Text Analytics.
Benefits of AI and ML in Cloud Computing
- AI and ML provide actionable insights and predictions for better decision-making.
- AI and ML automate tasks, increasing employee efficiency.
- AI engines personalize experiences, boosting satisfaction and engagement.
Use Cases
- Customer Support: AI-based chatbots and virtual assistants provide faster, more accurate responses to customer queries.
- Predictive Maintenance: ML models predict equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms can analyze transaction data in real time to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
Also read: The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Computing
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
These organizations are increasingly embracing multi-cloud, relying on services from more than one cloud provider to address the diversity of their needs. Such an approach brings flexibility in services, reduces the level of vendor lock-in, and creates opportunities to access the best features and prices available among the group of providers.
A hybrid cloud strategy combines both public and private cloud environments, thereby allowing businesses to derive benefits from the scalability and cost-effective features brought in by public clouds but still enjoy the courage of keeping sensitive data and critical workloads in private clouds.
Benefits of Multi-Cloud Strategies
- Flexibility: Tailored service selection for workloads.
- Risk Mitigation: Multi-cloud reduces downtime risks from single provider issues.
- Cost Optimization: Businesses can optimize costs by selecting cost-effective services from CSPs.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
- Scalability: Hybrid clouds scale like public clouds for non-sensitive workloads, while private clouds handle critical data and applications.
- Data Sovereignty: Sensitive data can be stored on-site or in a private cloud following government policies.
- Optimized Performance: Off-load workloads to the public cloud or private cloud for optimized performance and cost.
Use Cases
- Disaster Recovery: Hybrid cloud solutions offer ideal disaster recovery by mirroring data across public and private clouds.
- Data Security: Sensitive data can be stored in a private cloud while less-sensitive workloads run in public clouds.
- Bursting Workloads: Businesses can handle peak workloads by bursting into the public cloud, keeping performance levels steady during increased demand.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a category of cloud computing where a vendor handles the execution of a piece of code in reaction to a request and bills the customer based on the actual amount of resources consumed in the operation. In other words, developers can write the code, and the service provider should manage the infrastructure of a server.
Benefits of Serverless Computing
- Serverless computing allows developers to write code without worrying about infrastructure management.
- Resources automatically adapt to demand, optimizing performance.
- Customers pay for compute time, free when the system is down.
Key Serverless Services
- AWS Lambda: AWS Lambda allows developers to run any code in response to events without having to provision or manage the servers.
- Azure Functions: Azure Functions is a serverless compute service that allows for event-driven code execution.
- Google Cloud Functions: Google Cloud Functions lets you choose a runtime, write code, and trigger it with Google Cloud services or third-party tools. Perfect for serverless apps that need to run code in response to events.
- Real-Time Data Processing: Can be used in the processing of real-time data; for instance, in the analysis of sensor data or streaming data processing.
- Back End for Mobile and Web Apps: Enables scalable backends for mobile and web apps, handling data storage, authentication, and business logic.
Also read: Battle of the Clouds: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Face-Off!
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Businesses are becoming more confident in moving their operations to the cloud. Continuously, cloud providers are enhancing their security offerings in line with the changing threat landscape and compliance regulations.
Key Security Trends
- Zero Trust Architecture: Zero trust in cloud security ensures continuous verification of users and devices before accessing resources.
- AI-Driven Security: AI and ML detect and respond to security threats in real time. Cloud-based AI security services automate responses by analyzing patterns and identifying anomalies.
- Confidential Computing: Hardware-based Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) enables data protection through computation. Cloud providers develop confidential computing solutions for data protection.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory compliance is a great area of focus when it comes to operating a business within highly regulated industries, for example, in health care, finance, and government. A plethora of compliance certifications and services are provided by Cloud providers to assist the business in meeting compliance requirements.
Business Use Cases
- Data encryption: Cloud providers enable encryption services to be run on users’ data at rest and in transit, supporting data security and the mandated compliance initiatives.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM services enhance security by managing user identities and controlling cloud access, ensuring compliance.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Cloud SIEM solutions should provide real-time monitoring, threat detection, and rapid response to security incidents, allowing businesses to operate securely in the cloud.
Closing Thoughts
The cloud computing landscape has been changing based on changing technological landscapes and evolving business needs. In 2025, the cloud computing landscape, on the basis of the trends discussed above, will represent edge computing and 5G, the infusion of AI and ML, multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, serverless computing, and enhanced security and compliance.
Certainly, businesses are going to save interest in these trends and realign their strategies to harness opportunities that these new waves open up. Embracing these trends very much means optimizing their operational efficiency, enhanced capacity to make informed decisions, and gaining sustainable competitive advantages in the era of digitization.
But the real thing is going to be the synergy of cloud computing with other such emerging technologies: artificial intelligence, machine learning, and so on, that will keep triggering further innovative changes across industries. In other words, the future of cloud computing is unquestionably bright, and new possibilities and solutions are on the horizon. This is going to be very defining in its ability to create a new model of running business enterprises and delivering value to customers.
Also read: Dominating the Market with Cloud Power