Anything in some way alludes to the Internet can be a “web” – a website, a page, GPS, access, security, a camera… It isn’t shocking in light of the fact that the “web” is a part of the three “fantastic” WWW – World Wide Web – associated with sites on the network. However, this prefix additionally applies to numbers. This is the neglected Web 1.0. What’s more, Web 2.0, is certainly all the rage since it possesses a prevailing position. Furthermore, Web 3.0, which came into utilization quite recently utilized in specific circles, while still bashfully dislodging its predecessor.
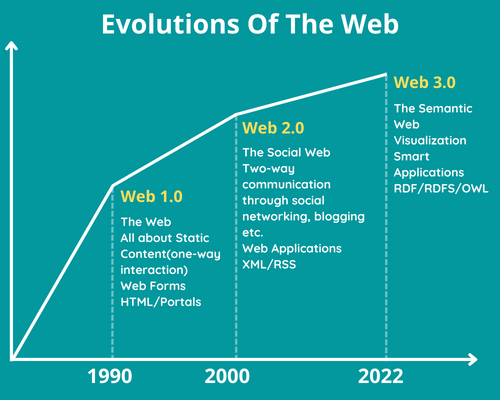
The World Wide Web has gone through different advances over the recent years and keeps on developing right up until now. With interest in Web 3.0 getting steam as blockchain, DAO (Decentralized autonomous organization), and security innovation become progressively popular, it means a lot to glance back at the previous generations and compare them.
Table of Contents
What is Web 2.0?
The second transformative phase of the web is portrayed particularly by the change from static pages to dynamic or user-created content and the beginning of social media.
Web 2.0 introduced a time when the web characterized itself as another medium. It was independent and particular from each and every other that went before it, including conventional print and video. Rather than simply static sites that pushed data to clients, Web 2.0 presented new types of intelligence. Ideas, for example, writing for a blog became famous, and social networks started to arise with Friendster, My Space, and in the end Facebook.
The utilization of CSS is one more principal attribute of Web 2.0. In the early time of the web, engineers needed to arrange pages with tables, which didn’t consider a lot of control. By the mid-2000s, CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) turned out to be more normal and all the more remarkable, empowering complex plan formats that significantly altered the manner in which the web looked.
Noticeable features of Web 2.0
- Access to web content from mobile phones, tablets, TVs, control centers, and, surprisingly, a kettle associated with the Internet.
- Dynamic content(rather than static original pages), which is intended to work in CTA mode.
- User engagement in content creation – users not just share and comment on articles and recordings yet, in addition, produce them themselves.
- During the time of data transmission, there is a particular “mediator” – a controlling platform.
- Advancement of API for interaction between various projects.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 addresses the next phase of the development of the web/internet and possibly could be as disruptive and address as large a change in outlook as Web 2.0 did. Web 3.0 is based upon the central ideas of decentralization, transparency, and more noteworthy client utility.
The term Web 3.0 goes beyond Semantic Web ideas embraced by the W3C and is all the more frequently utilized concerning more elevated-level ideas like decentralization. As opposed to the very centralized ways to deal with networks and information that are the premise of both Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, Web 3.0 is based on shared and agreement calculations as the establishment. A vital piece of the conveyed agreement for Web 3.0 comes in blockchain technology. There is no central power inside the association. Choices are executed through recommendations and casting a ballot, this guarantees decency and correspondence among its proprietors. Permitting everybody to include a voice inside the DAO.
Push for decentralization with Web 3.0 additionally incorporates digital currency/cryptocurrency, which gives one more choice for payments and money transfers. Additionally, the idea of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) gives one more method for making, overseeing, and claiming assets utilizing blockchain innovation.
Noticeable features of Web 3.0
- Semantic Web: All data is put away in a decentralized way by frameworks and people. Content is produced, shared, and unraveled through search and examination to make them justifiable on the grounds that the data introduced in numbers or keywords is of no utilization.
- Connectivity: Because of web semantic metadata, data is turning out to be more associated, permitting clients to get to all the vital data. During this cycle, the information stays independent. Consequently, projects can understand and explain data, permitting clients to really engage with machines.
- Universality: Different applications can get to the content on the grounds that each gadget is associated with the web. Hence, anybody can utilize the services anyplace.
- AI- Artificial intelligence: One of the fundamental highlights of Web 3.0 is that it integrates AI with the web, empowering PCs to grasp data like people. More intelligent frameworks will assist clients with coming by quicker and more exact outcomes.
- 3D Graphics Integration: 3D designs are an essential piece of sites and services in Web 3.0. Be it internet-based business, gaming, or land business, 3D innovation is making advances all over.
- Blockchain-enabled: Web 3.0 is truly blockchain-enabled and works on NFT, DAO, CIO, Bitcoin Cash, and Ethereum.
Read More: Best Blockchain Development Companies
Web 3.0 V/S Web 2.0
The universe of Web 1.0 was generally static and about giving data. With Web 2.0, the web has become dynamic and social. With Web 3.0, the web will become more astute and more dispersed than ever. The table beneath helps separate the critical contrasts between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0.
| S.No | Web 3.0 | Web 2.0 |
| 1 | Decentralized Edge computing shared and distributed consensus progressively become the standard in Web 3.0 | Centralized Application delivery, cloud services, and platform are represented and managed by centralized authorities |
| 2 | Metaverse world With Web 3.0, metaverse will arise to merge physical, virtual, and augmented reality | Social networks Web 2.0 introduced the period of informal social communication, including Facebook |
| 3 | NFTs Clients can get one-of-a-kind tokens that are relegated to value or give some type of advantage | Cookies The utilization of cookies assists with following clients and gives personalization |
| 4 | Blockchain Web 3.0 utilizes blockchain permanent ledger innovation. | Social information bases Databases support the content and utilization of Web 2.0 |
| 5 | Digital Crypto Currency Exchanges can be subsidized with encrypted digital currencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum | Fiat Currency Payments and exchanges happen with official money, like $USD |
| 6 | Artificial intelligence More astute, independent innovation, including AI and ML, will characterize Web 3.0 | CSS and Ajax Web 2.0 is characterized by layout technologies that give more unique control than Web 1.0 |
Key Takeaways
To ease the comprehension of the internet or web revolution, we can involve the analogy of revolution in films. If Web 1.0 addressed the high contrast film or movie era and Web 2.0 addressed the color film improved with 3D experience, then, at that point, Web 3.0 would be addressed by the vivid encounters in the metaverse.
We had seen that Web 2.0 upset the traditional physical organizations and yet gave huge open opportunities. Organizations that neglected to change had underrated the scale and the speed of progress and were too delayed to even consider adjusting to the new web-driven business model. Organizations that effectively made the change turned into disruptors in reshaping their enterprises and received immense rewards.
The center highlights of Web 3.0 are automation and decentralization, trustless and permissionless, network and ubiquity, and AI-ML. The decentralized framework and application platforms would move the power away from the tech giants and check them from taking advantage of the web clients’ information singularly for their own advantage.
To know more facts about technology stay tuned with us.
In any case, if you need any assistance with app development and software solutions reach us at CDN Solutions Group

